Have you ever wondered how double exposures are done in digital cameras? I have. Back in film days, we knew that to double expose a frame, all you needed to do is rewind it back to the frame you have just exposed, thereby taking two separate shots using one frame of the film. Nowadays with digital SLRs, there is no film to re-expose and no rewind mechanism to go back to a previous photo so you can re-shoot on top of it. However, double exposure and multiple exposures can be done in post-production quite easily. But this little tutorial will focus on how to take double exposure in-camera using a digital camera.

Equipment needed for double exposures
What you will need:
- A tripod.
- Your camera.
- Remote trigger, receiver or transceiver.
- Flash guns (speedlights) or strobes (one or two).
- Some light modifiers (optional) such as umbrellas, softboxes, or octaboxes.
- A backdrop or wall.
For my experiment below, I used two strobes mounted on stands and modified by gridded octaboxes. I used Paul Buff’s Cybersyncs for the wireless remote transceiver system. I also had three backdrops: one black, one beige and one patterned. See the image below for my studio setup and an iPhone picture of behind the scenes.

The camera and flash settings
The strobes were kept on a constant setting and I chose the lowest power. My ISO was also on the lowest setting (ISO 100) for most of the shots except for the f/16 ones where I cranked it up a little. The aperture varied between f/8 – f/16, depending on the look I was after and the length of my exposure. Shutter speed also varied between one second to a few seconds, to bulb. In other words, experiment until you get the look right.
How to take the double exposure
This is the trick. While the camera is exposing the image so that the shutter is open, keep triggering the flash. For these shots, I triggered the flash 2-4 times depending on the length of the exposure and how fast I could press the trigger button. The flash freezes the action so the more time the flash fires the more frozen actions you get on your image.
This leads us nicely to the first tip.
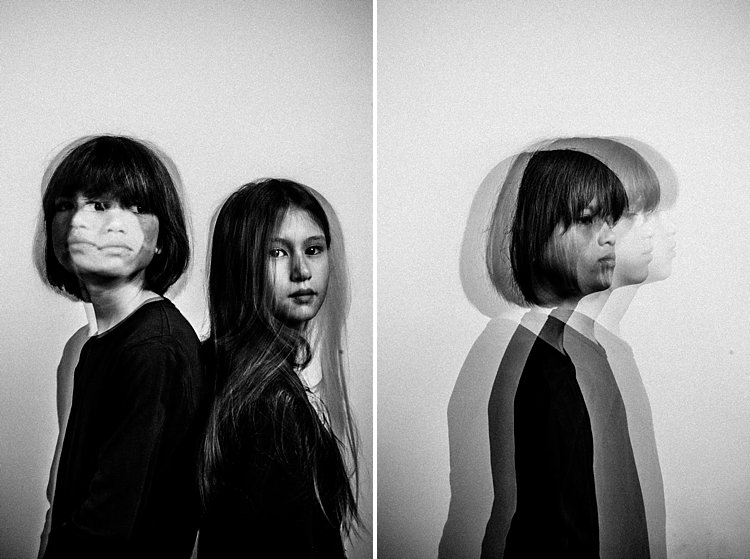
#1 Exaggerated movement is key

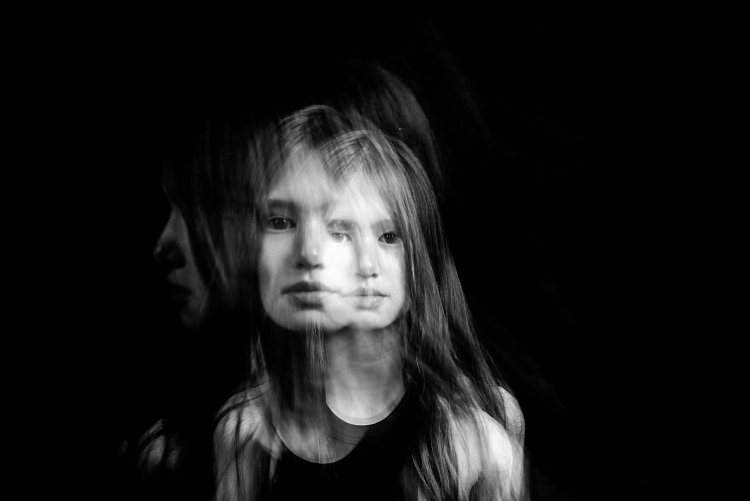
If your subject makes very small and minor movements, the likelihood is the images will sit on top of each other. This may result in one final image that looks like a blurry mess as in the photo above rather than many separate frozen images on a single photo as shown in the photo below. It is better to tell your subject to move distinctly away from the first position so the movements are separate. The camera still captures the trail of movement as a blur. But when you trigger the flash, that particular moment is rendered sharp and still.
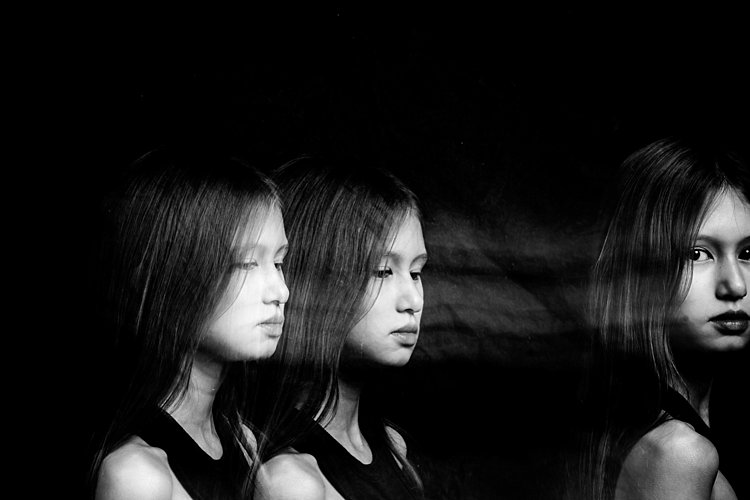

I asked my kids to walk across the frame, counting each step and on a certain count to turn their heads. I would trigger the flash when they moved sideways or turned their heads. At other times I asked one of the children to only join the frame on the third flash so that there is only one of her that registers. I also got them to walk towards me (see photo at top of article). It was at that stage that I changed my aperture to the smallest my lens allowed, in this case, f/16 so that I could still get the head sharp at various depths of field.
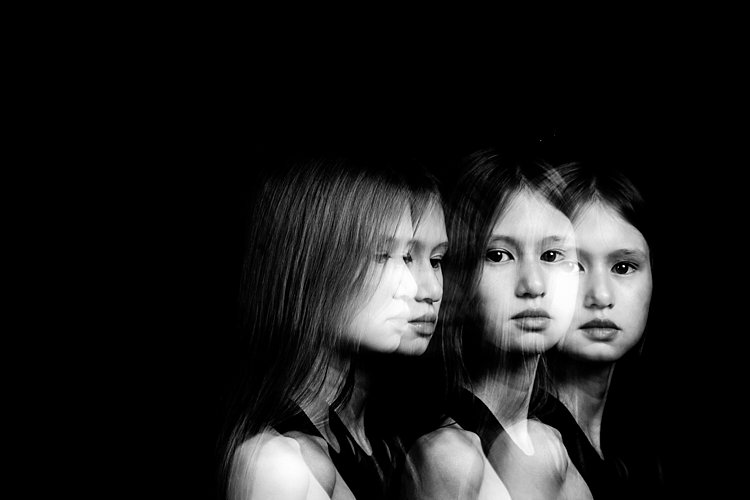
In the photo below, I got my kids to shake their heads as fast and as many times as they could. I wanted the focus here to be the movement rather than their frozen faces. Don’t be afraid to experiment. The beauty of digital is that unlike film, you have an infinite number of frames at your disposal so can afford to make many mistakes until you get what you are looking for.
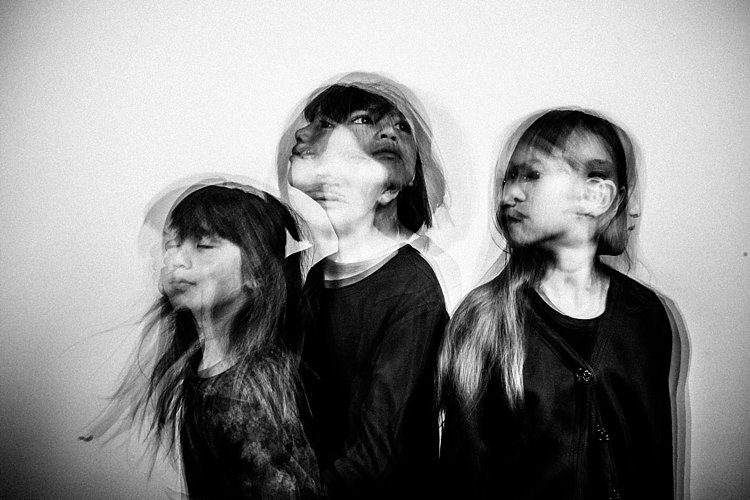

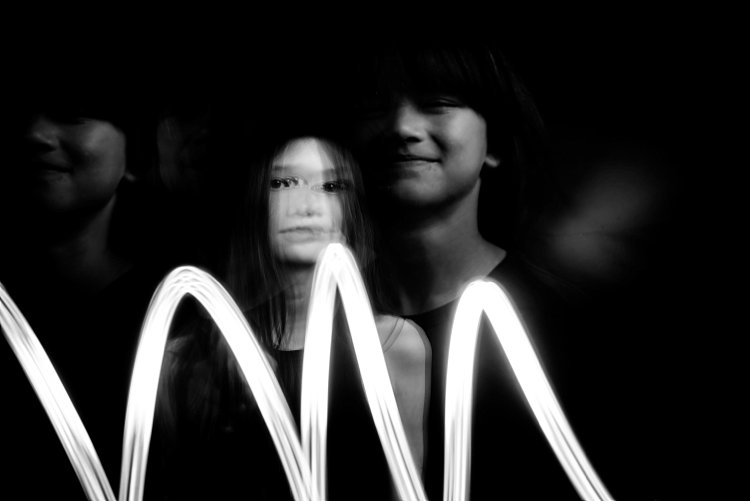
#2 A dark background is better
Compare the image above with the light background to the other images with the black background. The difference in the final image is vast. I prefer the dark background where my intention was to freeze several portraits and the lighter background where my focus was on capturing the trail of movements. Overall I shot and preferred more of the images with a dark background as the delineation between actions and the clarity of subjects are easier to see. Contrast between the skin and other lighter parts of the image was also easier to achieve compared to images shot with the beige background. In the photo below, I edited quite aggressively to get the contrast I wanted. I also added grain to simulate a film look.

#3 Experiment with materials and textures
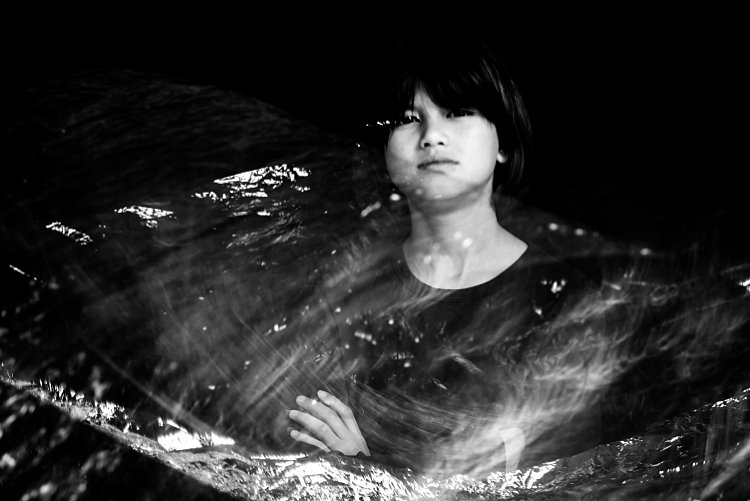
Bring in other materials such as aluminum foil. This one here is an emergency blanket. Two of my kids stood on either side, held and waved the blanket up and down in front of the middle child so the slow shutter captured some of the movement of the foil. The kids also carried a torch (flash light) and did some light painting. The problem I found with both photos was the blurry look of their faces. Because they did not do big movements with their bodies, hence the frozen photos captured by each flash just got stacked up in roughly the same spot. Other things you can use are glow sticks, flashing lights, moving lights, iPhone and iPad screens – pretty much anything that reflects or emits light.
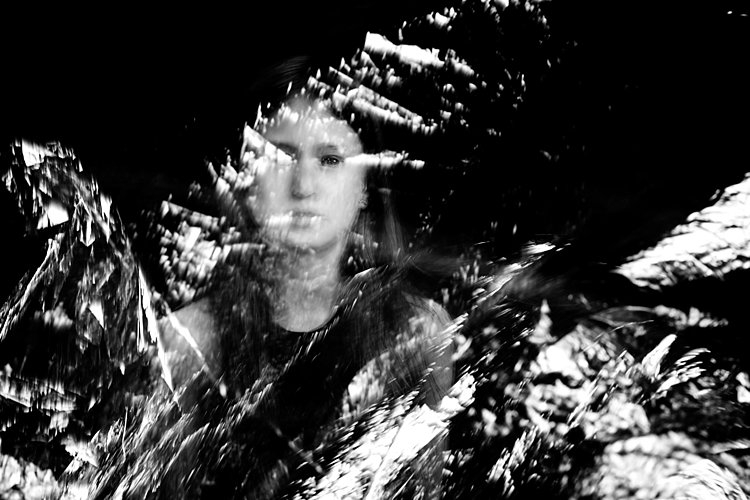

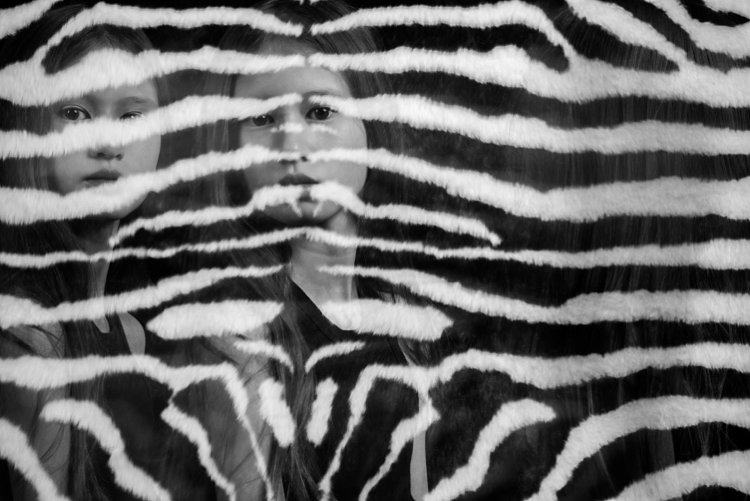
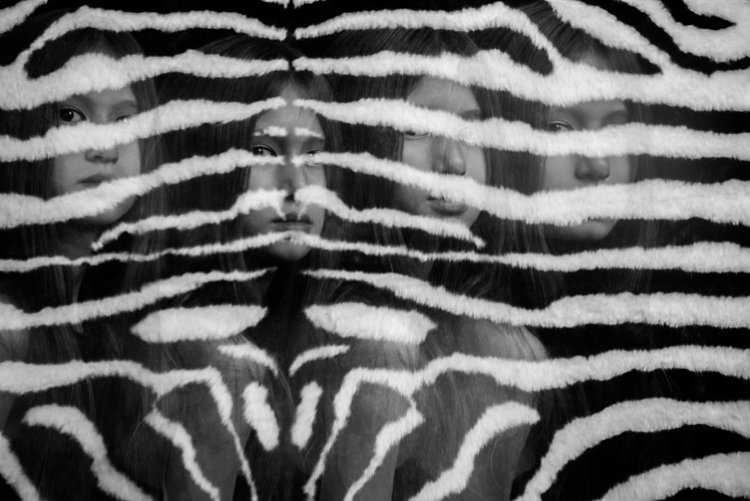
Don’t be afraid to experiment with backgrounds too. In the photos below, I changed the background to a zebra striped black and white rug just because I wanted to see what would happen. I used the same movement techniques as above and the same camera and light settings but the results were very different and unique. The last image below was a happy accident. My third child popped her head up on the third flash, but she came closer to the camera than I had intended so the flash didn’t quite illuminate her face enough. However, I thought this looked really effective as it provided the gray tone of the image as well as a solid form in the middle thereby making the overall image more dynamic and interesting.
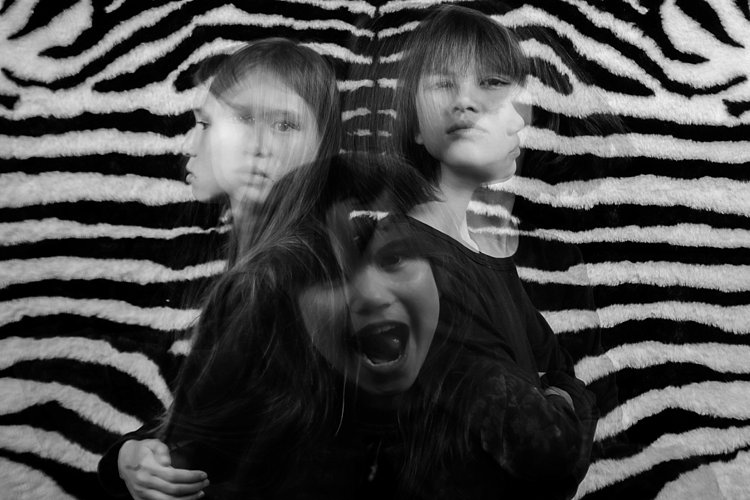


I hope you enjoyed this little tutorial on in-camera double exposures using flash. If you have more ideas, do share them here in the comments below!
The post 3 Tips for Creating Double Exposures In-Camera Using Flash by Lily Sawyer appeared first on Digital Photography School.